AVHRR Level 1B Metop Global - Data Access
This notebook demonstrates how to search and access Metop data using HDA and how to read, process and visualize it using satpy.
To search and access DEDL data a DestinE user account is needed
DestinE Data Lake (DEDL) Harmonized Data Access (HDA) documentation
This notebook uses Satpy
© 2014–2025 PyTroll community
Licensed under PyGNU GPL v3
This notebook demonstrates how to search and access Metop data using HDA and how to read, process and visualize it using satpy
The Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR) operates at 5 different channels simultaneously in the visible and infrared bands. Channel 3 switches between 3a and 3b for daytime and nighttime. As a high-resolution imager (about 1.1 km near nadir) its main purpose is to provide cloud and surface information such as cloud coverage, cloud top temperature, surface temperature over land and sea, and vegetation or snow/ice.
Throughout this notebook, you will learn:
Authenticate: How to authenticate for searching and access DEDL collections.
Search: How to search DEDL data using datetime and bbox filters.
Download: How to download DEDL data through HDA.
Read and visualize Metop AVHRR data: How to load process and visualize Metop AVHRR data using Satpy.
Authenticate¶
import destinelab as deauthimport requests
import json
import os
from getpass import getpassDESP_USERNAME = input("Please input your DESP username or email: ")
DESP_PASSWORD = getpass("Please input your DESP password: ")
auth = deauth.AuthHandler(DESP_USERNAME, DESP_PASSWORD)
access_token = auth.get_token()
if access_token is not None:
print("DEDL/DESP Access Token Obtained Successfully")
else:
print("Failed to Obtain DEDL/DESP Access Token")
auth_headers = {"Authorization": f"Bearer {access_token}"}Please input your DESP username or email: eum-dedl-user
Please input your DESP password: ········
Response code: 200
DEDL/DESP Access Token Obtained Successfully
Response code: 200
DEDL/DESP Access Token Obtained Successfully
Search¶
HDA endpoint¶
HDA API is based on the Spatio Temporal Asset Catalog specification (STAC), it is convenient define a costant with its endpoint.
HDA_STAC_ENDPOINT="https://hda.data.destination-earth.eu/stac/v2"COLLECTION_ID = "EO.EUM.DAT.METOP.AVHRRL1"search_response = requests.post(HDA_STAC_ENDPOINT+"/search", headers=auth_headers, json={
"BBox": [-5 ,31,20,51],
"collections": [COLLECTION_ID],
"datetime": "2024-07-04T11:00:00Z/2024-07-04T13:00:00Z"
})
The first item in the search results
from IPython.display import JSON
JSON(search_response.json()["features"][0])Download¶
We can download now the returned data.
from tqdm import tqdm
import time
import zipfile
#number of products to download:
nptd=1
# Define a list of assets to download
for i in range(0,nptd,1):
product=search_response.json()["features"][i]
download_url = product["assets"]["downloadLink"]["href"]
print(download_url)
filename = "downloadLink"
response = requests.get(download_url, headers=auth_headers)
total_size = int(response.headers.get("content-length", 0))
print(f"downloading {filename}")
with tqdm(total=total_size, unit="B", unit_scale=True) as progress_bar:
with open(filename, 'wb') as f:
for data in response.iter_content(1024):
progress_bar.update(len(data))
f.write(data)
zf=zipfile.ZipFile(filename)
with zipfile.ZipFile(filename, 'r') as zip_ref:
zip_ref.extractall('.')https://hda-download.lumi.data.destination-earth.eu/data/eumetsat/EO.EUM.DAT.METOP.AVHRRL1/AVHR_xxx_1B_M03_20240704095203Z_20240704113103Z_N_O_20240704112753Z/downloadLink
downloading downloadLink
409MB [00:01, 406MB/s]
del responseSatpy¶
The Python package satpy supports reading and loading data from many input files. For Metop data in the native format, we can use the satpy reader ‘avhrr_l1b_eps’.
pip install --quiet satpy pyspectralNote: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.
import os
from glob import glob
import xarray as xr
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.colors
from matplotlib.axes import Axes
from packaging.version import Version
import satpy
from satpy.scene import Scene
print(satpy.__version__)
if Version(satpy.__version__) < Version("0.57"):
from satpy.composites import GenericCompositor
from satpy.writers import to_image
from satpy.resample import get_area_def
elif Version(satpy.__version__) == Version("0.57"):
from satpy.composites import GenericCompositor
from satpy.area import get_area_def
else:
from satpy.composites.core import GenericCompositor
from satpy.area import get_area_def
from satpy import available_readers
from satpy import MultiScene
import pyresample
import pyspectral
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
warnings.simplefilter(action = "ignore", category = RuntimeWarning)
satpy_installation_path=satpy.__path__
delimiter = ""
satpy_installation_path = delimiter.join(satpy_installation_path)0.59.0
Read and load data¶
Single scene¶
We can use the Scene constructor from the satpy library, a Scene object represents a single geographic region of data. Once loaded we can list all the available bands (spectral channel) for that scene.
filenames = glob('./AVHR_xxx_1B_M0*.nat')
#len(filenames)# read the last file in filenames
scn = Scene(reader='avhrr_l1b_eps', filenames=[filenames[-1]])
# print available datasets
scn.available_dataset_names()['1',
'2',
'3a',
'3b',
'4',
'5',
'cloud_flags',
'latitude',
'longitude',
'satellite_azimuth_angle',
'satellite_zenith_angle',
'solar_azimuth_angle',
'solar_zenith_angle']We can then load the first and the second spectral channels and have a look to some info
# load
scn.load(['1','2'], calibration='reflectance')
scn['1']scn['1'].attrs['wavelength']WavelengthRange(min=0.58, central=0.63, max=0.68, unit='µm')Do some calculation¶
Calculations based on loaded datasets/channels can easily be assigned to a new dataset.
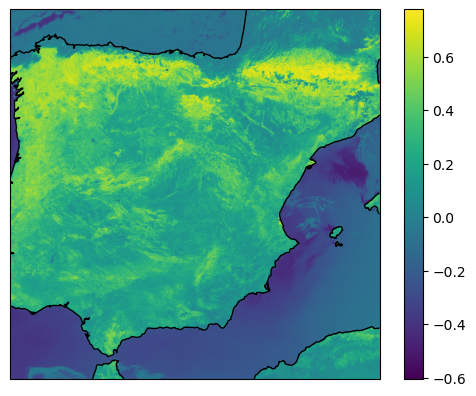
We resample the scene in a smaller area over the Spain and use the 2 loaded datasets to calculate a new dataset.
newscn = scn.resample('spain')newscn["ndvi"] = (newscn['2'] - newscn['1']) / (newscn['2'] + newscn['1'])
#scn.show("ndvi")Visualize datasets¶
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pyresample.kd_tree import resample_nearest
from pyresample.geometry import AreaDefinition
from pyresample import load_area
area_def = load_area(satpy_installation_path+'/etc/areas.yaml', 'spain')
#scene
lons, lats = newscn["1"].area.get_lonlats()
swath_def = pyresample.geometry.SwathDefinition(lons, lats)ndvidata = newscn["ndvi"].chunk({'y': 512, 'x': 512})
ndvi=ndvidata.data.compute()
#ndvi = newscn["ndvi"].data.compute()
result = resample_nearest(swath_def, ndvi, area_def, radius_of_influence=20000, fill_value=None)
#cartopy
crs = area_def.to_cartopy_crs()
fig, ax = plt.subplots(subplot_kw=dict(projection=crs))
coastlines = ax.coastlines()
ax.set_global()
#plot
img = plt.imshow(result, transform=crs, extent=crs.bounds, origin='upper')
cbar = plt.colorbar()